Prof. Dr. Goutam Guha (M.S., M.Ch)
Consultant Plastic, Cosmetic and Reconstructive Surgeon.

Consultant Plastic, Cosmetic and Reconstructive Surgeon.

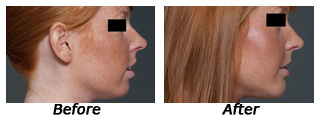
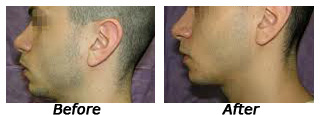
Mentoplasty
Mentoplasty is the surgery of the chin which along with the nose helps in contouring the facial profiles.
Chin augmentation is to balance the face by altering a weak or obtrusive chin. Hence the relationship between the chin and the rest of the face should, in theory, achieve a sort of harmony. Depending on the patients' needs, the change in their appearance can either be subtle or astonishing. Consultation with a doctor is necessary to find the specifics that will better suit your needs.
The surgery usually takes about an hour to perform. This is actually one of the quicker cosmetic surgeries when compared to some of the others. Surgical incisions will be made in the necessary areas of the chin inside the mouth. A lot of surgeons use endoscopy during the surgery to be more precise during operation. This is one of the newer technological tools for plastic surgeons-it utilizes a camera to better see the patient's tissues and muscles. Patients can expect minimal scarring, Augmentation can be done by bony osteotomy or silastic implants or hydroxyappetite a bone supplement.
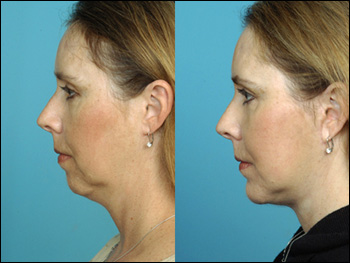
Mentoplasty may be done for several reasons:
. To correct malformations of the chin resulting from developmental abnormalities of the bones in the jaw. Sometimes the jawbones continue to grow on one side of the face but not the other, leading to facial asymmetry. In other instances a part of the jawbone is missing; this condition is known as congenital agenesis of the jaw.
. To reshape a chin that is out of proportion to other facial features.
. As part of gender reassignment surgery. The size and shape of the chin and lower jawline are somewhat different in men and women. Some people choose to have mentoplasty as part of their gender transition.
. As part of craniofacial reconstruction following trauma or cancer surgery.
. As part of orthognathic surgery. Orthognathic surgery involves repositioning the facial bones in order to correct deformities that affect the patient's ability to speak or chew normally.