Q. What is bone marrow?
Bone marrow is a spongy tissue found inside bones. The bone marrow in the breast bone, skull, hips, ribs and spine contains stem cells that produce the body's blood cells. These blood cells include white blood cells (leukocytes), which fight infection; red blood cells (erythrocytes), which carry oxygen to and remove waste products from organs and tissues; and platelets, which enable the blood to dot.
Q. Why transplant?
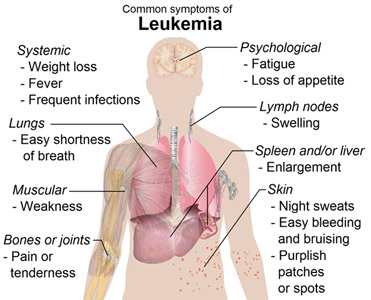
In patients with leukemia, aplastic anemia, and some immune deficiency diseases, the stem cells in the bone marrow malfunction, producing an excessive number of defective or immature blood cells (in the case of leukemia) or low blood cell counts (in the case of aplastic anemia). The immature or defective blood cells interfere with the production of normal blood cells, accumulate in the bloodstream and may invade other tissues.
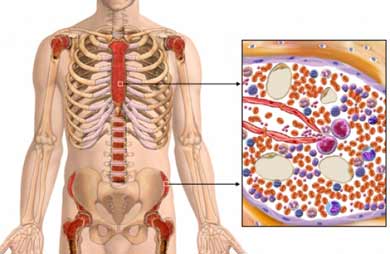 Large doses of chemotherapy and/or radiation are required to destroy the abnormal stem cells and abnormal blood cells. These therapies, however, not only kill the abnormal cells but can destroy normal cells found in the bone marrow as well. Similarly, aggressive chemotherapy used to treat some lymphomas and other cancers can destroy healthy bone marrow. A bone marrow transplant enables physicians to treat these diseases with aggressive chemotherapy and/or radiation by allowing replacement of the diseased or damaged bone marrow after the chemotherapy/radiation treatment. Large doses of chemotherapy and/or radiation are required to destroy the abnormal stem cells and abnormal blood cells. These therapies, however, not only kill the abnormal cells but can destroy normal cells found in the bone marrow as well. Similarly, aggressive chemotherapy used to treat some lymphomas and other cancers can destroy healthy bone marrow. A bone marrow transplant enables physicians to treat these diseases with aggressive chemotherapy and/or radiation by allowing replacement of the diseased or damaged bone marrow after the chemotherapy/radiation treatment.
While bone marrow transplants do not provide 100 percent assurance that the disease will not recur, a transplant can increase the likelihood of a cure or at least prolong the period of disease-free survival for many patients.
Types of transplants
In a bone marrow transplant, the patient's diseased bone marrow is destroyed and healthy marrow is infused into the patient's blood-stream. In a successful transplant, the new bone marrow migrates to the cavities of the large bones, engrafts and begins producing normal blood cells.
If bone marrow from a donor is used, the transplant is called an "allogeneic" BMT, or "syngeneic" BMT if the donor is an identical twin. In an allogeneic BMT, the new bone marrow infused into the patient must match the genetic makeup of the patient's own marrow as perfectly as possible. Special blood tests are conducted to determine whether or not the donor's bone marrow matches the patient's. If the donor's bone marrow is not a good genetic match, it will perceive the patient's body as foreign material to be attacked and destroyed. This condition is known as graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and can be life-threatening. Alternatively, the patient's immune system may destroy the new bone marrow. This is called graft rejection.
There is a 35 percent chance that a patient will have a sibling whose bone marrow is a perfect match. If the patient has no matched sibling, a donor may be located in one of the international bone marrow donor registries, or a mis-matched or autologous transplant may be considered.
In some cases, patients may be their own bone marrow donors. This is called an autologous BMT and is possible if the disease afflicting the bone marrow is in remission or if the condition being treated does not involve the bone marrow (e.g. breast cancer, ovarian cancer, Hodgkin's disease, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and brain tumors). The bone marrow is extracted from the patient prior to transplant and may be "purged" to remove lingering malignant cells (if the disease has afflicted the bone marrow).
Preparing for the transplant
A successful transplant requires the patient be healthy enough to undergo the rigors of the transplant procedure. Age, general physical condition, the patient's diagnosis and the stage of the disease are all considered by the physician when determining whether a person should undergo a transplant.
Prior to a bone marrow transplant, a battery of tests is carried out to ensure the patient is physically capable of undergoing a transplant. Tests of the patient's heart, lung, kidney and other vital organ functions are also used to develop a patient "baseline" against which post-transplant tests can be compared to determine if any body functions have been impaired. The pre-transplant tests are usually done on an outpatient basis.
A successful bone marrow transplant requires an expert medical team - doctors, nurses, and other support staff - who are experienced in bone marrow transplants, can promptly recognize problems and emerging side effects, and know how to react swiftly and properly if problems do arise. A good bone marrow transplant program will also recognize the importance of providing patients and their families with emotional and psychological support before, during and after the transplant, and will make personal and other support systems readily available to families for this purpose.
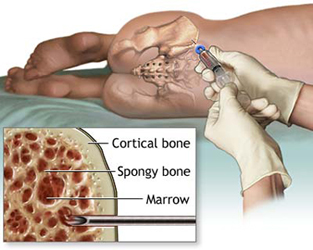
Bone marrow harvest
Regardless of whether the patient or a donor provides the bone marrow used in the transplant, the procedure used to collect the marrow - the bone marrow harvest - is the same. The bone marrow harvest takes place in a hospital operating room, usually under general anesthesia. It involves little risk and minimal discomfort.
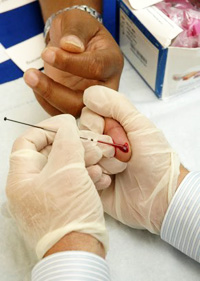
While the patient is under anesthesia, a needle is inserted into the cavity of the rear hip bone or "iliac crest" where a large quantity of bone marrow is located. The bone marrow a thick, red liquid - is extracted with a needle and syringe. Several skin punctures on each hip and multiple bone punctures are usually required to extract the requisite amount of bone marrow. There are no surgical incisions or stitches involved - only skin punctures where the needle was inserted.  The amount of bone marrow harvested depends on the size of the patient and the concentration of bone marrow cells in the donor's blood. Usually one to two quarts of marrow and blood are harvested. While this may sound like a lot, it really only represents about 2% of a person's bone marrow, which the body replaces in four weeks. The amount of bone marrow harvested depends on the size of the patient and the concentration of bone marrow cells in the donor's blood. Usually one to two quarts of marrow and blood are harvested. While this may sound like a lot, it really only represents about 2% of a person's bone marrow, which the body replaces in four weeks.
When the anesthesia wears off, the donor may feel some discomfort at the harvest site. The pain will be similar to that associated with a hard fall on the ice and can usually be controlled with Tylenol. Donors who are not also the BMT patient are usually discharged after an overnight stay and can fully resume normal activities in a few days.
For autologous transplants, the harvested bone marrow will be frozen (cryopreserved) and stored at a temperature between -80 and -196 degrees centigrade until the day of transplant. It may first be "purged" to remove residual cancerous cells that can't be easily identified under the microscope (see page 30).
In allogeneic BMTs, the bone marrow may be treated to remove "T-cells" (T cell depletion) to reduce the risk of graft-versus-host disease (see page 94). It will then be transferred directly to the patient's room for infusion.
Preparative regimen
A patient admitted to the bone marrow transplant unit will first undergo several days of chemotherapy and/or radiation which destroys bone marrow and cancerous cells and makes room for the new bone marrow. This is called the conditioning or preparative regimen. The exact regimen of chemotherapy and/or radiation varies according to the disease being treated and the "protocol" or preferred treatment plan of the facility where the BMT is being performed.
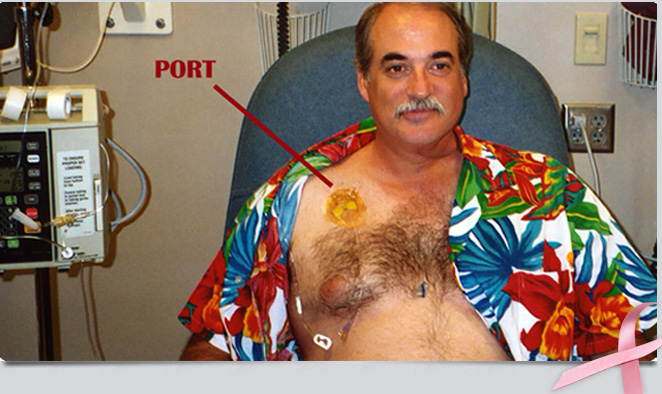
Prior to conditioning, a small flexible tube called a catheter (sometimes called a "Hickman®" or central venous line) will be inserted into a large vein in the patient's chest just above the heart. This tube enables the medical staff to administer drugs and blood products to the patient painlessly, and to withdraw the hundreds of blood samples required during the course of treatment without inserting needles into the patient's arms or hands.
The dosage of chemotherapy and/or radiation given to patients during conditioning is much stronger than dosages administered to patients with the same disease who are not undergoing a BMT. Patients may become weak, irritable and nauseous. Most BMT centers administer anti-nausea medications to minimize discomfort.
The transplant
A day or two following the chemotherapy and/or radiation treatment, the transplant will occur. The bone marrow is infused into the patient intravenously in much the same way that any blood product is given. The transplant is not a surgical procedure. It takes place in the patient's room, not an operating room.
Patients are checked frequently for signs of fever, chills, hives and chest pains while the bone marrow is being infused. When the transplant is completed, the days and weeks of waiting begin.
Engraftment
The two to four weeks immediately following transplant are the most critical. The high-dose chemotherapy and/or radiation given to the patient during conditioning will have destroyed the patient's bone marrow, crippling the body's "immune" or defense system. As the patient waits for the transplanted bone marrow to migrate to the cavities of the large bones, set up housekeeping or "engraft," and begin producing normal blood cells, he or she will be very susceptible to infection and excessive bleeding. Multiple antibiotics and blood transfusions will be administered to the patient to help prevent and fight infection. Transfusions of platelets will be given to prevent bleeding. Allogeneic patients will receive additional medications to prevent and control graft-versus-host disease.
Extraordinary precautions will be taken to minimize the patient's exposure to viruses and bacteria. Visitors and hospital personnel will wash their hands with antiseptic soap and, in some cases, wear protective gowns, gloves and/or masks while in the patient's room. Fresh fruits, vegetables, plants and cut flowers will be prohibited in the patient's room since they often carry fungi and bacteria that pose a risk of infection. When leaving the room, the patient may wear a mask, gown and gloves as a barrier against bacteria and virus, and as a reminder to others that he or she is susceptible to infection. Blood samples will be taken daily to determine whether or not engraftment has occurred and to monitor organ function. When the transplanted bone marrow finally engrafts and begins producing normal blood cells, the patient will gradually be taken off the antibiotics, and blood and platelet transfusions will generally no longer be required. once the bone marrow is producing a sufficient number of healthy red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets, the patient will be discharged from the hospital, provided no other complications have developed. BMT patients typically spend four to eight weeks in the hospital.
Q. What a patient feels during the transplant?
A bone marrow transplant is a physically, emotionally, and psychologically taxing procedure for both the patient and family. A patient needs and should seek as much help as possible to cope with the experience. "Toughing it out" on your own is not the smartest way to cope with the transplant experience.
The bone marrow transplant is a debilitating experience. Imagine the symptoms of a severe case of the flu - nausea, vomiting, fever, diarrhea, extreme weakness. Now imagine what it's like to cope with the symptoms not just for several days, but for several weeks. That approximates what a BMT patient experiences during hospitalization.
During this period the patient will feel very sick and weak. Walking, sitting up in bed for long periods of time, reading books, talking on the phone, visiting with friends or even watching TV may require more energy than the patient has to spare.
Complications can develop after a bone marrow transplant such as infection, bleeding, graft-versus-host disease, or liver disease, which can create additional discomfort. The pain, however, is usually controllable by medication. In addition, mouth sores can develop that make eating and swallowing uncomfortable. Temporary mental confusion sometimes occurs and can be quite frightening for the patient who may not realize it's only temporary. The medical staff will help the patient deal with these problems.
 Handling emotional stress Handling emotional stress
In addition to the physical discomfort associated with the transplant experiance there is emotional and psychological discomfort as well. Some patients find the emotional and psychological stress more problematic than the physical discomfort.
The psychological and emotional stress stems from several factors. First, patients undergoing transplants are already traumatized by the news that they have a life-threatening disease. While the transplant offers hope for their recovery, the prospect of undergoing a long, arduous medical procedure is still not pleasant and there's no guarantee of success.
Second, patients undergoing a transplant can feel quite isolated. The special precautions taken to guard against infection while the immune system is impaired can leave a patient feeling detached from the rest of the world and cut off from normal human contact. The patient is housed in a private room, sometimes with special air-filtering equipment to purify the air. The number of visitors is restricted and visitors are asked to wear gloves, masks and/or other protective clothing to inhibit the spread of bacteria and virus while visiting the patient. When the patient leaves the room, he or she may be required to wear a protective mask, gown and/or gloves as a barrier against infection. This feeling of isolation comes at the very time in a patient's life when familiar surroundings and close physical contact with family and friends are most needed.
'Helplessness" is also a common feeling among bone marrow transplant patients, which can breed further feelings of anger or resentment. For many, it's unnerveing to be totally dependent on strangers for survival, no matter how competent they may be. The fact that most patients are unfamiliar with the medical jargon used to describe the transplant procedure compounds the feeling of helplessness. Some also find it embarrassing to be dependent on strangers for help with basic daily functions such as using the washroom.
The long weeks of waiting for the transplanted marrow to engraft, for blood counts to return to safe levels, and for side effects to disappear increase the emotional trauma. Recovery can be like a roller coaster ride: one day a patient may feel much better, only to awake the next day feeling as sick as ever.
Leaving the hospital
After being discharged from the hospital, a patient continues recovery at home (or at lodging near the transplant center if the patient is from out of town) for two to four months. Patients usually cannot return to full-time work for up to six months after the transplant.
Though patients will be well enough to leave the hospital, their recovery will be far from over. For the first several weeks the patient may be too weak to do much more than sleep, sit up, and walk a bit around the house. Frequent visits to the hospital or associated clinic will be required to monitor the patient's progress, and to administer any medications and/or blood products needed. It can take six months or more from the day of transplant before a patient is ready to fully resume normal activities.
During this period, the patient's white blood cell counts are often too low to provide normal protection against the viruses and bacteria encountered in everyday life. Contact with the general public is therefore restricted. Crowded movie theaters, grocery stores, department stores, etc. are places recovering BMT patients avoid during their recuperation. Often patients will wear protective masks when venturing outside the home.
A patient will return to the hospital or clinic as an outpatient several times a week for monitoring, blood transfusions, and administration of other drugs as needed. Eventually, the patient becomes strong enough to resume a normal routine and to look forward to a productive, healthy life.
Life after transplant
It can take as long as a year for the new bone marrow to function normally. Patients are closely monitored during this time to identify any infections or complications that may develop.
Life after transplant can be both exhilarating and worrisome. On the one hand, it's exciting to be alive after being so close to death. Most patients find their quality of life improved after transplant.
Nonetheless, there is always the worry that relapse will occur. Furthermore, innocent statements or events can sometimes conjure up unpleasant memories of the transplant experience long after the patient has recovered. It can take a long time for the patient to come to grips with these difficulties.
Q. Is it worth it?
Yes! For most patients contemplating a bone marrow transplant, the alternative is near-certain death. Despite the fact that the transplant can be a trying experience, most find that the pleasure that comes from being alive and healthy after the transplant is well worth the effort. |
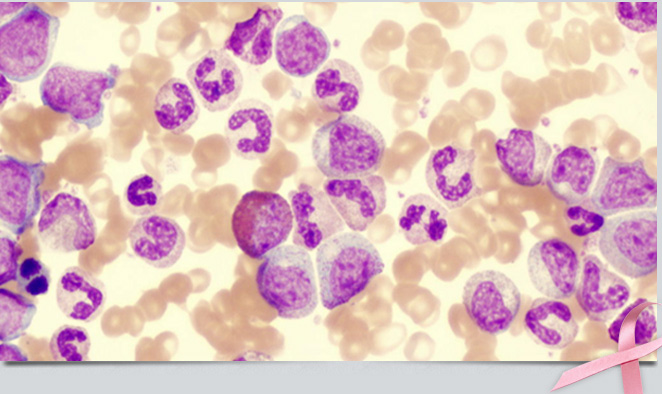
 puncture) checks for leukemia cells in the fluid that fills the spaces in and around the brain and spinal cord (cerebrospinal fluid). Chest x-rays can reveal signs of disease in the chest.
puncture) checks for leukemia cells in the fluid that fills the spaces in and around the brain and spinal cord (cerebrospinal fluid). Chest x-rays can reveal signs of disease in the chest. cancer. These include:
cancer. These include:
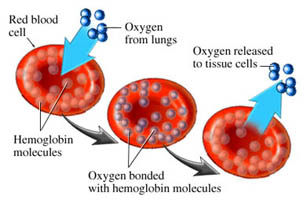
 Large doses of chemotherapy and/or radiation are required to destroy the abnormal stem cells and abnormal blood cells. These therapies, however, not only kill the abnormal cells but can destroy normal cells found in the bone marrow as well. Similarly, aggressive chemotherapy used to treat some lymphomas and other cancers can destroy healthy bone marrow. A bone marrow transplant enables physicians to treat these diseases with aggressive chemotherapy and/or radiation by allowing replacement of the diseased or damaged bone marrow after the chemotherapy/radiation treatment.
Large doses of chemotherapy and/or radiation are required to destroy the abnormal stem cells and abnormal blood cells. These therapies, however, not only kill the abnormal cells but can destroy normal cells found in the bone marrow as well. Similarly, aggressive chemotherapy used to treat some lymphomas and other cancers can destroy healthy bone marrow. A bone marrow transplant enables physicians to treat these diseases with aggressive chemotherapy and/or radiation by allowing replacement of the diseased or damaged bone marrow after the chemotherapy/radiation treatment. The amount of bone marrow harvested depends on the size of the patient and the concentration of bone marrow cells in the donor's blood. Usually one to two quarts of marrow and blood are harvested. While this may sound like a lot, it really only represents about 2% of a person's bone marrow, which the body replaces in four weeks.
The amount of bone marrow harvested depends on the size of the patient and the concentration of bone marrow cells in the donor's blood. Usually one to two quarts of marrow and blood are harvested. While this may sound like a lot, it really only represents about 2% of a person's bone marrow, which the body replaces in four weeks. Handling emotional stress
Handling emotional stress