It is just forty years that Human Sexual Response has been scientifically documented after making scientific observations, under actual conditions, on human beings. William H. Masters and Virginia E. Johnson (M & J) first published their book on "Human Sexual Response" in April 1966. Prior to this, text books of physiology dismissed this subject with a brief reference saying that the male involvement was restricted to erection, penetration and ejaculation and so far as the female partner is concerned, she is a passive partner. Though much of what M & J described was already known even to common man, the pioneering work showed the importance of experimentation, observation and documentation. It is just forty years that Human Sexual Response has been scientifically documented after making scientific observations, under actual conditions, on human beings. William H. Masters and Virginia E. Johnson (M & J) first published their book on "Human Sexual Response" in April 1966. Prior to this, text books of physiology dismissed this subject with a brief reference saying that the male involvement was restricted to erection, penetration and ejaculation and so far as the female partner is concerned, she is a passive partner. Though much of what M & J described was already known even to common man, the pioneering work showed the importance of experimentation, observation and documentation.
The research population was originally selected from commercial sex workers but was later on shifted to volunteers, 382 females and 312 males. While actual observations were made on all these study subjects. Intravaginal observations were made by using artificial coital equipment which could take intravaginal photographs on line.
They were able to find one common pattern in both males and females which they described as the sexual cycle. The common pattern was that the sexual cycle could in both sexes be divided into four specific phases which they called :
- Excitement phase
- Plateau phase
- Orgasm phase
- Resolution phase.
 They also observed that physiological changes were not restricted to the genitalia. They classified the changes occurring during a sexual cycle into genital and extragenital changes. They also observed that 'Physiologic reactions to sexual stimulation are superficial and/or deep vasocongestion and both generalized and specific myotonia. They also observed that physiological changes were not restricted to the genitalia. They classified the changes occurring during a sexual cycle into genital and extragenital changes. They also observed that 'Physiologic reactions to sexual stimulation are superficial and/or deep vasocongestion and both generalized and specific myotonia.
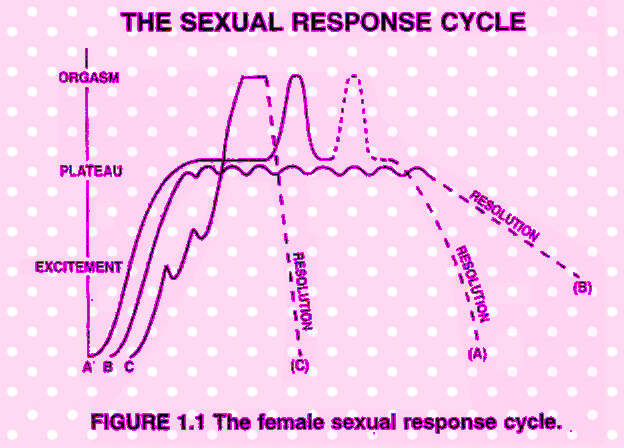
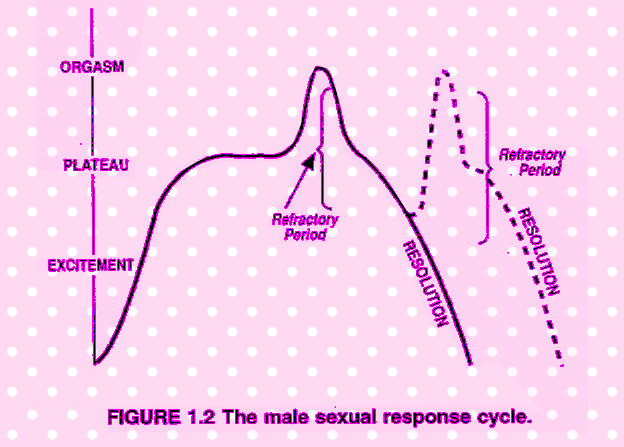
THE SEXUAL RESPONSE CYCLE (Fig. 1.1, Fig. 1.2)
- Excitement Phase response develops from any physical or mental stimulation of an erotic nature. The phase may be prolonged or cut short.
If the phase is prolonged it merges into the second phase.
- Plateau Phase. This phase continues for a variable length of time with continued and effective stimulation and culminates into the third phase.
 |
| |
A - All Four Stages: Multiple Orgasm
B - Do Not Reach Orgasm - Slow Resolution
C - Rapid Response Cycle. |
| |
 |
- Orgasmic Phase which lasts for only a few seconds. Whether the cycle reaches the orgasmic phase or is aborted.
- Resolution Phase This is the final phase. This arbitrary division is a good matrix in which various physiologic changes can be fitted.
FEMALE GENITAL RESPONSES
 Labia Majora Labia Majora
Responses of labia majora are different in nulliparous and parous women. In nullipara the labia become flatter and thinner. They are also raised upwards and outwards in late excitement and plateau phase. No further changes occur during orgasmic phase. In parous women they undergo vasocongestion and may increase two or three fold in size. If orgasm is experienced they reduce in size rapidly otherwise it may take a long time for them to detumesce.
Labia Minora
They increase in size during excitement and plateau phase and protrude beyond the labia majora. Thus the length of vaginal barrel is increased by about one centimeter. They also undergo colour changes from pink to bright red during plateau phase. This is due to vasocbngestion.
Bartholin's Glands
They are located in labia minora and secrete a mucoidal liquid mostly during plateau phase. It plays minimal role in lubrication but may play a role in reducing vaginal acidity.
 Clitoris Clitoris
This unique organ has the only purpose of receiving and transmitting sensuous stimulii. Its reactions have been fully studied in detail and many variations have been observed. During excitement phase there is a tumescence of clitoral glans in most cases. During plateau phase the glans and shaft withdraw from the pudendal hanging position and retract against the anterior border of symphysis pubis. Congestion of hood of the clitoris covers up the clitoris during plateau phase giving an impression that it has become smaller in size. No specific reaction occurs during orgasmic phase. Retraction of clitoris disappears within few seconds of starting of resolution phase but decongestion of clitoral shaft may take from five to thirty minutes.
Vagina
Within seconds of sexual stimulation lubrication occurs in vagina due to
production of a transudate by the vaginal walls. This is believed to be due to
vasodilatation of vessels round about the vaginal barrel, during the excitement
phase and is not continued during the plateau phase. This lubrication also occurs
in women who have undergone total hysterectomy and in women with artificial
vagina.
 Vagina which is normally a potential space has capacity to expand. During excitement phase there is lengthening and distension of inner two thirds of the vagina. In addition the uterus is pulled up and back in to the false pelvis. The diameter of the vaginal barrel increases from 2 cm to 6 cm at the level of cervix. Total length of vagina increases from 7 cm to 10 cm during excitement phase. During this phase the vaginal walls undergo colour changes due to vasocongestion causing a darkening. The rugal pattern of vaginal mucosa is flattened due to distension. During plateau phase there is marked congestion of the lower third of vagina. This area of plateau phase congestion has been named as orgasmic platform. The plateau phase is thus marked by full vaginal expansion, uterine elevation, and formation of orgasmic platform. During orgasmic phase the orgasmic platform area contracts strongly in a regular recurring pattern at intervals of 0.8 seconds about three to fifteen times with each orgasm. During resolution phase all these changes are gradually reversed. Vagina which is normally a potential space has capacity to expand. During excitement phase there is lengthening and distension of inner two thirds of the vagina. In addition the uterus is pulled up and back in to the false pelvis. The diameter of the vaginal barrel increases from 2 cm to 6 cm at the level of cervix. Total length of vagina increases from 7 cm to 10 cm during excitement phase. During this phase the vaginal walls undergo colour changes due to vasocongestion causing a darkening. The rugal pattern of vaginal mucosa is flattened due to distension. During plateau phase there is marked congestion of the lower third of vagina. This area of plateau phase congestion has been named as orgasmic platform. The plateau phase is thus marked by full vaginal expansion, uterine elevation, and formation of orgasmic platform. During orgasmic phase the orgasmic platform area contracts strongly in a regular recurring pattern at intervals of 0.8 seconds about three to fifteen times with each orgasm. During resolution phase all these changes are gradually reversed.
All these changes have a functional role in reproduction. Ballooning of vagina near the fornix produces space for a seminal pool in which the cervix dips during the resolution phase.
Uterus
 The uterus shows three basic responses during sexual cycles. First is the uterine elevation reaction which tends to become more vertical as the cycle moves through its various stages. The uterus which is a pelvic organ is elevated to be in the false pelvis. The cervix shows hardly any change except that its mouth becomes a little wider during orgasmic phase. The corpus of the uterus does not show any contractions till the subject experiences orgasm. These contractions may result in pain during orgasm in some individuals. The concept of sucking effect on seminal fluid has not been substantiated by experiments of M&J. The uterus shows three basic responses during sexual cycles. First is the uterine elevation reaction which tends to become more vertical as the cycle moves through its various stages. The uterus which is a pelvic organ is elevated to be in the false pelvis. The cervix shows hardly any change except that its mouth becomes a little wider during orgasmic phase. The corpus of the uterus does not show any contractions till the subject experiences orgasm. These contractions may result in pain during orgasm in some individuals. The concept of sucking effect on seminal fluid has not been substantiated by experiments of M&J.
FEMALE EXTRAGENITAL RESPONSES
Breasts
During excitement phase the first change is erection of nipples. Second change is increased venous engorgement shown by more visible venous pattern all over the breast. Third change is increase in the size of the breast, more apparent if she is lying down. During plateau phase there is vasocongestion and engorgement of areola giving impression that the nipples have become smaller. There is no specific reaction of breast in orgasmic phase. Nipple erection, areolar tumescence, prominent vascular network and increase in size are all at the peak. There are differences between suckled and non suckled breasts. All these changes gradually regress during resolution phase.
Sex Flush
Pinkish spots appear below the breasts and these may spread all over the breasts and even all over the body. They will be obviously more visible in individuals with a fair skin. This vasocongestion in the skin does not occur in all individuals and not everytime. It starts in later part of excitement phase, peaks during plateau and rapidly disappears after orgasm iii reverse order of its appearance.
Myotonia
Increase in the tone of various muscles, both voluntary and involuntary starts during the excitement phase. Spasmodic contractions of muscles all over the body are observed especially visible in muscles activating fingers and toes in plateau phase. Contractions of gluteal muscles both voluntary and involuntary are observed in plateau and orgasmic phase. The muscle tension is rapidly lost during resolution phase.
 Respiration, Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Respiration, Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
During plateau phase respiratory rate may increase to 40, heart rate up to 180 beats per minute and systolic blood pressure may rise by 30 to 80 mm Hg and diastolic by 20 to 40 mm/Hg. In females higher figures are recorded during masturbation than during coitus. All these changes rapidly neturn to normal in resolution phase.
Perspiration
Most females perspire during the resolution phase and also report a feeling of warmth all oyer the body.
MALE GENITAL RESPONSES
Penis
First physiologic response to effective sexual stimulation is penile erection. During prolonged excitement phase erection may be partially lost and again regained many times. Erection may be partially or completely lost due to extraneous stimulii. During plateau phase there may be a minor increase in diameter as orgasmic phase approaches, especially near the corona glandis. A colour change may also appear late in this phase. Superficial veins may be visible and a few drops of Cowper's gland secretion appear at the tip of the penis. Orgasmic phase ejaculatory reaction develops from regularly occurring contractions of sphincter urethrae, bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernosus and superficial and deep perineal muscles. The entire penile urethra contracts to force the seminal fluid out under pressure. Expulsive contractions start at intervals of 0.8 seconds and then become slower. During resolution phase the involution occurs in two phases. Primary stage which reduces penis size by 50% occurs with extreme rapidity. The remaining detumescence takes time. No clinically recognised difference was observed between circumcised and uncircumcised males.
 Testis Testis
During excitement phase both testis get elevated towards the perineum, due to involuntary contraction of cremasteric muscle. They also rotate anteriorly. During plateau phase they are tightly apposed to the perineum. Full elevation is pathognomonic of impending ejaculation. No additional changes are observed during orgasmic phase. During resolution phase there is a loss of vasocongestion and descent back into the scrotum.
Scrotum
During excitement phase there is tensing and thickening of scrotal integuments due to vasocongestion and contraction of dartos layer. There are no further changes during plateau and orgasmic phase, during resolution phase there is either a slow or rapid return to normal.
MALE EXTRAGENITAL REACTIONS
 Breasts Breasts
Responses are inconsistent. Nipple erection may occur in 60% of subjects during excitement and plateau phase. There is no specific reaction during orgasmic phase.
Sex Flush
Sex flush similar to females appears in 25% of males. It may not occur during every sexual cycle.
Myotonia
Increased muscle tension is observed in all phases of sexual cycle, groups of muscles being affected depends on sexual positioning. For example carpopedal spasm occurs in supine position but not in other positions.
 Rectum Rectum
External rectal sphincter contracts irregularly on direct stimulation and contracts at the rate of 0.8 seconds during orgasm.
Cardiorespiratory Reactions
Hyperventilation, tachycardia and rise in blood pressure in a manner similar to those in females during all three stages.
Perspiratory Reaction
Many males show involuntary sweating after ejaculation, whether there is physical exertion or not. Usually this reaction is confined to palms of hand and soles of feet but may occur on other parts of body also. |