Prof. Dr. Goutam Guha (M.S., M.Ch)
Consultant Plastic, Cosmetic and Reconstructive Surgeon.

Consultant Plastic, Cosmetic and Reconstructive Surgeon.
Hair Transplant
Hair loss, or alopecia, is very common. Many conditions can cause it. Hair loss is divided into two categories:
. Scarring, which leads to permanent destruction of the hair follicle
. Nonscarring, in which hair follicles remain intact
The vast majority of hair loss is nonscarring. It includes such conditions as pattern baldness and telogen effluvium, or excessive hair shedding.
The majority of hair loss in both men and women is pattern baldness, also referred to as androgenetic alopecia. Both genetic (family) and hormonal factors play a role in pattern baldness.
Another common cause of hair loss is excessive hair shedding. Common triggers for hair shedding include a major illness, surgery, rapid weight loss, nutritional deficiency, thyroid problems, stress, and certain medications.
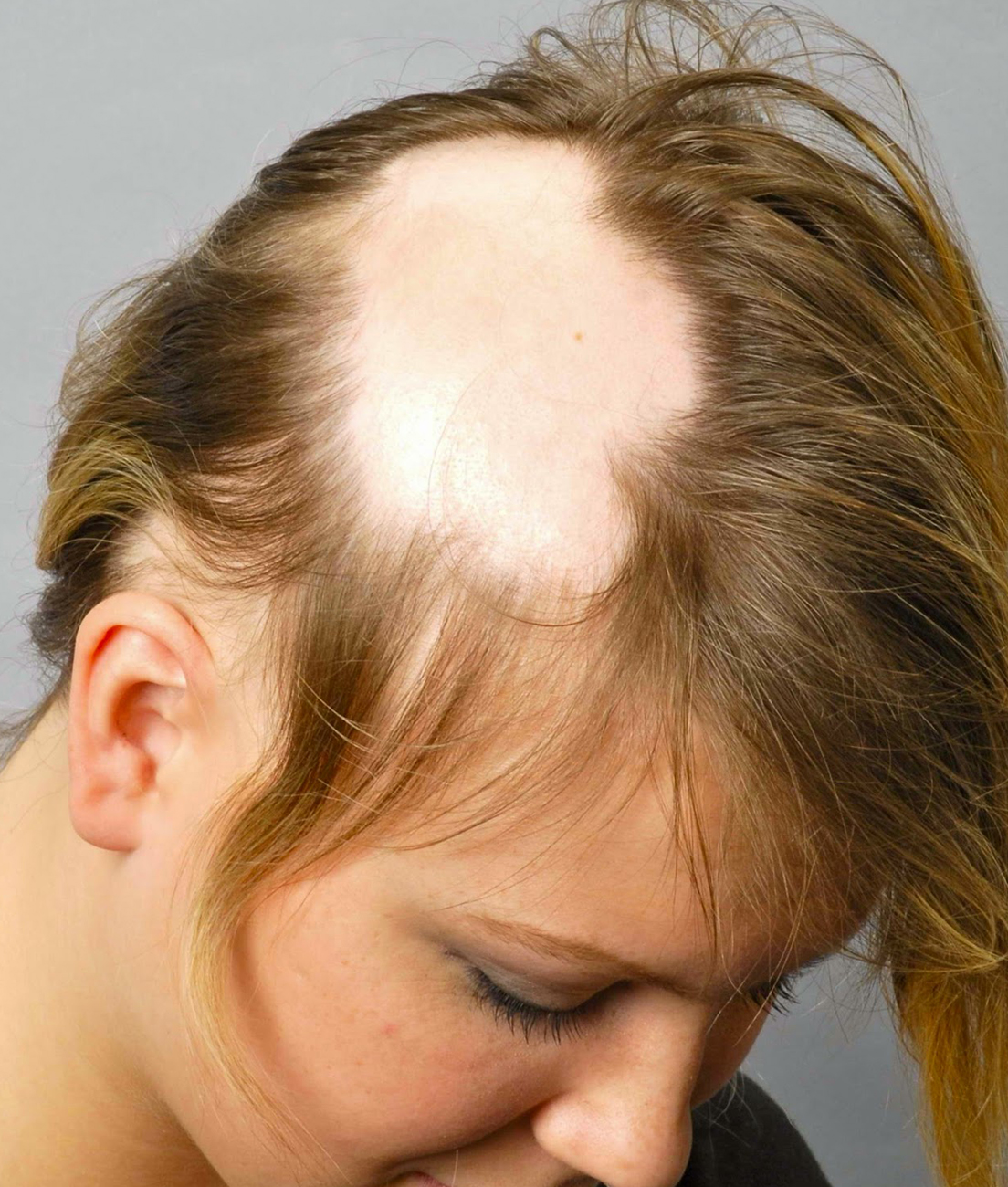
Hair Transplant What can cause hair loss?
. Medications, vitamins, or minerals: medications used to treat high blood pressure, heart problems, depression or gout; chemotherapy or radiation treatment for cancer patients; and in some cases, unusually high levels of vitamin A or low levels of iron or protein. For women, birth control pills can cause hair loss.
. Illness, including thyroid disease and severe infection
. Scalp conditions, including psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, and folliculitis
. Trauma, including traction alopecia resulting from certain hair styles that cause trauma to the hair follicles, and trichotillomania, or repetitive pulling and breaking of one's own hair.
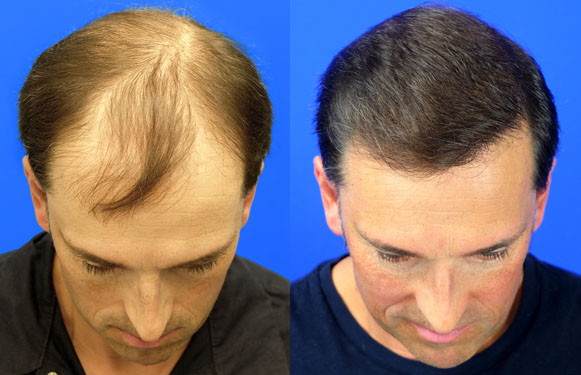
Who is a candidate for hair replacement?
. Men with male-pattern baldness
. Some women with thinning hair
. A person who has lost some but not all hair as a result of burns or other scalp injuries
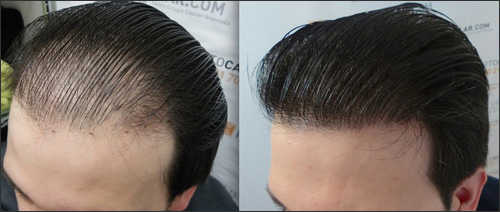
What Happens During a Hair Transplant?
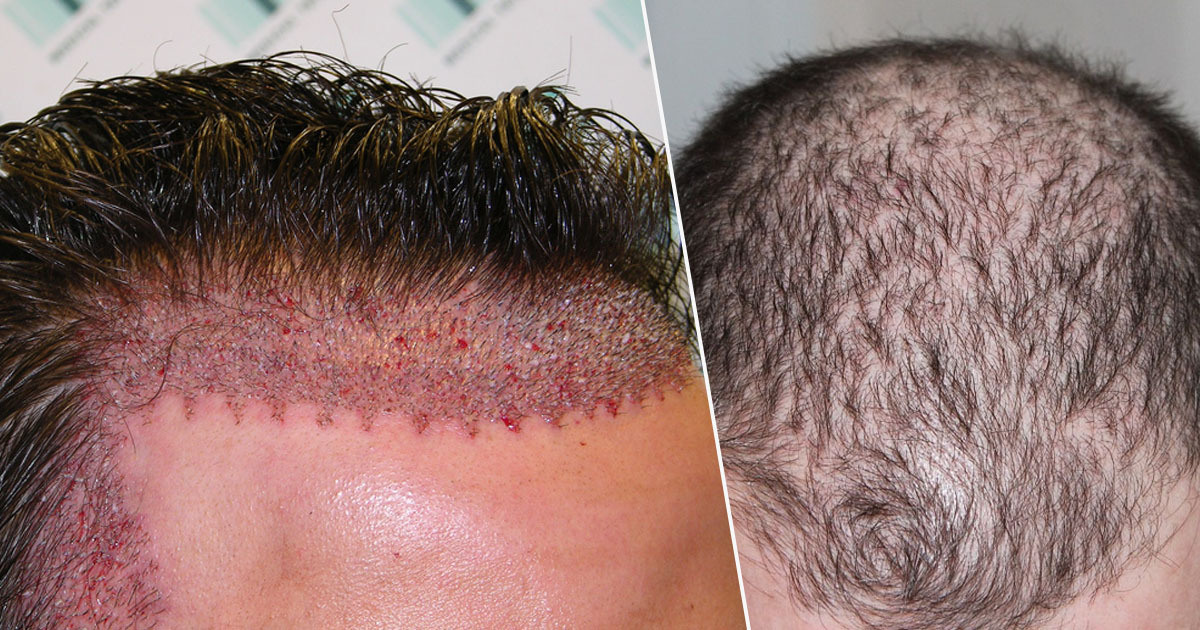
After thoroughly cleaning your scalp, a surgeon will use a small needle to numb an area of your head with local anesthesia. Next, they'll use a scalpel to remove a round section of your scalp covered with hair. Then they'll sew the scalp closed.
The surgeon will separate the removed portion of scalp into small sections using a magnifying lens and sharp surgical knife. When implanted, these sections will help achieve natural-looking hair growth.
The surgeon will make tiny holes with a blade or needle in the area of your scalp receiving the hair transplant. They'll gently place hairs in these holes. During one treatment session, a surgeon may transplant hundreds or even thousands of hairs.
After the graft, gauze or bandages will cover your scalp for a few days. A hair transplant session can take four hours or more.
Your stitches will be removed about 10 days after surgery. You may require up to three or four sessions to achieve the full head of hair you desire. Sessions occur several months apart to allow each transplant to fully heal.
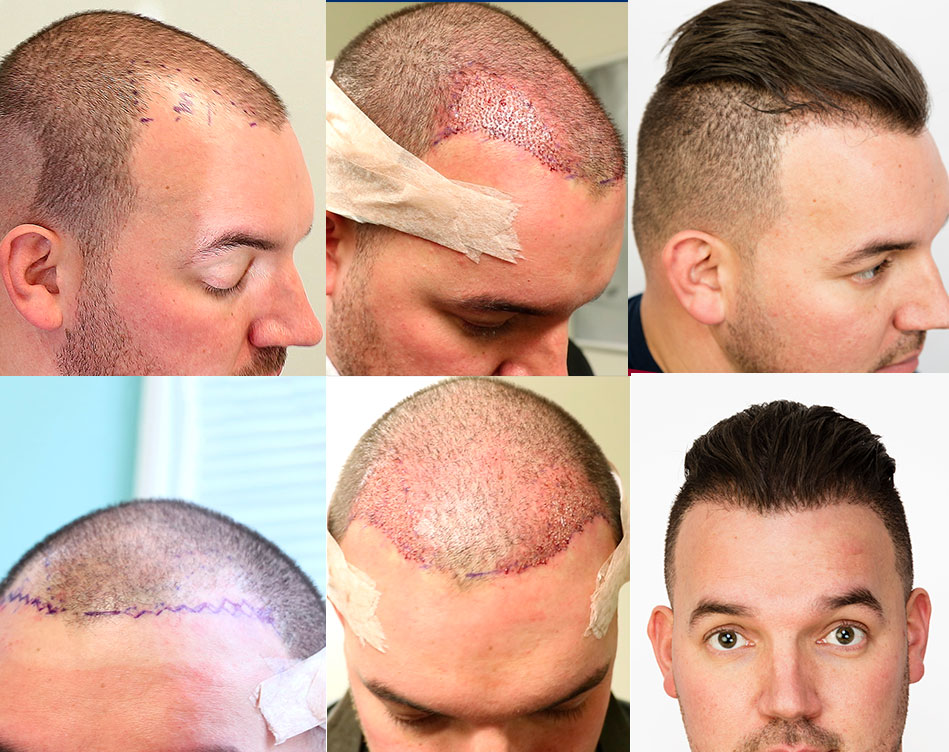
What Happens After a Hair Transplant?
Your scalp may be sore and you may need to take medications following hair transplant surgery, such as:
. pain medication
. antibiotics to reduce your risk of infection
. anti-inflammatory medications to keep swelling down
. Most people can return to work several days after surgery.
It's normal for the transplanted hair to fall out two to three weeks after the procedure. This makes way for new hair growth. Most people will see about 60 percent new hair growth six to nine months after surgery.
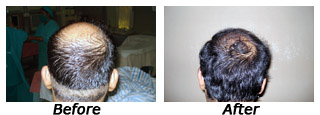
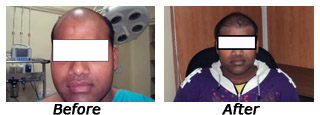
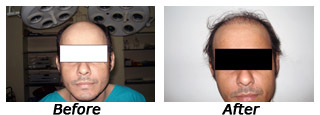
Picture Gallery