 |
• Allogeneic stem cell transplantation -
A form of treatment whereby a patient first receives high dose chemotherapy (myeloablative transplant) and then has stem cells given from a donor who is closely genetically matched (sibling or unrelated volunteer). |
|
| |
 |
• Anaemia (in over 16 years of age) -
Anaemia is a lack of red cells or low haemoglobin level in the blood. It can be caused either by reduced production of red cells by the bone marrow, by increased destruction of red cells in the blood stream or due to blood loss.
Aplastic anaemia is a bone marrow condition whereby not enough blood cells are made. Typically patients are anaemic but all blood counts can be effected.
Haemolytic anaemia is caused by increased destruction of red cells which maybe due to antibodies in the blood.
Hereditary anaemia is an abnormality of haemoglobin production due to inherited genetic abnormalities. These include thalassaemia, sickle-cell disease and also other red cell disorders for example hereditary spherocytosis. |
|
| |
 |
• Autologous stem cell transplantation -
Autologous stem cell transplantation is a form of treatment whereby the patient’s own stem cells are re-infused after high dose chemotherapy. |
|
| |
 |
• Bleeding Disorders -
Bleeding disorders can be caused by problems in the clotting machinery of the blood when one or more factors are either not produced or abnormally produced due to usually inherited problem of genetic abnormality. |
|
| |
 |
• Cytogenetics -
An area of medicine which studies the change in the body’s chromosomes which occurs as part of many blood cancers. |
|
| |
 |
• Cytotoxics -
Chemical substances which are toxic to cells. They have direct anti tumour activity but can also affect normal cells, thereby giving side effects. |
|
| |
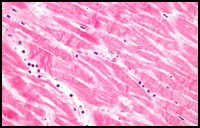 |
• Histopathology -
A pathology discipline where a specialist consultant makes a diagnosis from a tissue biopsy. The tissue is stained to identify different types of cells and then examined under a microscope. |
|
| |
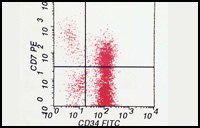 |
• Immunophenotyping -
This is a technique which identifies different protein on the surface of the cells. It uses antibodies which are labelled with fluorochromes (fluorescent paint). These labelled cells with antibodies are processed and can give the diagnosis on blood, bone marrow, spinal fluid and other body fluids. The results can be obtained quickly, within same day. |
|
| |
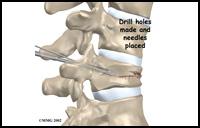 |
• Kyphoplasty -
A procedure performed through the skin by injecting bone cement into fractured vertebrae. The aim of the procedure is to relieve the pain caused by the fracture. It maybe considered for patients with multiple myeloma. |
|
| |
 |
• Leukaemia -
Leukaemia is a cancer of the white cells. The word ‘leukaemia’ is derived from Greek and means white cell ‘leuk’ in the blood ‘aemia’.
Acute leukaemia is an aggressive form which need prompt treatment with chemotherapy, but this is also means that the response to chemotherapy is good and the treatment may be curative.
Chronic leukaemia is a term describing an increased level of white cells in the peripheral blood. There are many types including chronic myeloid leukaemia, chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia, mantle cell lymphoma, hairy cell leukaemia.
The disease is usually staged and assessed on a case to case basis to see whether it requires therapy. This is generally not a curative form of leukaemia, but considered a chronic disease which may be well controlled with treatment. |
|
| |
 |
• Lymphoma -
Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymph glands caused by abnormal white cells. It can be chronic (low grade) or have an acute presentation (high grade lymphoma). Chronic lymphoma can be indolent, slow growing and does not always needing treatment. High grade lymphoma presents rapidly, is fast growing, needs treatment shortly after diagnosis and usually responds well to chemotherapy. |
|
| |
 |
• Hodgkin Lymphoma -
Hodgkin lymphoma is a type cancer originating from white cells causing lymph node swelling. It requires treatment with chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Many patients with this lymphoma can be cured. |
|
| |
 |
• Myelodysplasia -
This is a group of blood disorders in which the bone marrow is ineffective at producing blood cells. It may evolve to acute leukaemia. |
|
| |
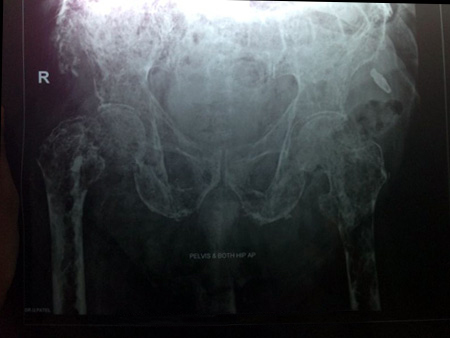 |
• Multiple Myeloma -
Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer arising from plasma cells which are found in the bone marrow. It is associated with production of an abnormal antibody called paraprotein. At the very early level it is diagnosed as an MGUS which stands for monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance. However, not all the patients with MGUS will eventually develop myeloma. |
|
| |
 |
• Myeloproliferative disorders -
Myeloproliferative disorders are disorders of an overactive bone marrow whereby red cells, white cells or platelets are produced in excess of normal requirements causing high levels detectable on a blood count. If the red cells are increased it is called polycythaemia and if platelets are increased it is caused essential thrombocythaemia. Not all patients with polycythaemia have an underlying myeloprolifertive disease. |
|
| |
 |
• Myelofibrosis -
This is one of the myeloproliferative disorders where the bone marrow becomes scarred (fibrosis). Often the blood counts are low and the spleen may become enlarged |
|
| |
 |
• Neutropenia -
Neutropenia is a reduction in the number of neutrophils. This can be caused either by drugs, cyclical, autoimmune causes, lack of vitamins, antibodies against neutrophils or could be a first sign of a bone marrow abnormalities. Usually the patient is asymptomic however it may lead to recurrent infections |
|
| |
 |
• Radiology -
A medical specialty which utilises either x-ray, ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for diagnosis or staging, frequently Radiologists will perform biopsies under the guidance of ultrasound or CT (computer tomography) scans. |
|
| |
 |
• Thrombosis -
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in the blood vessel, either an artery or a vein. It can be caused by inherited problems in the clotting cascade reduced mobility, obstruction of the blood vessel or due to presence of abnormal antibodies. |
|
| |
 |
• VTE (Venous Thrombo Embolism) -
A term describing a blood clot (thrombus) in a vein. |
|