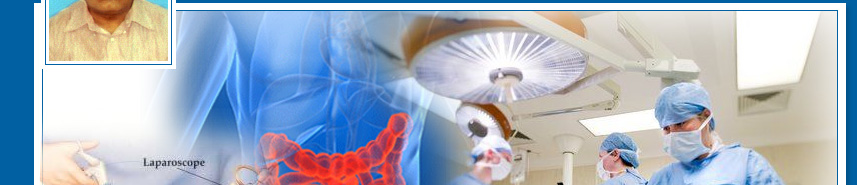
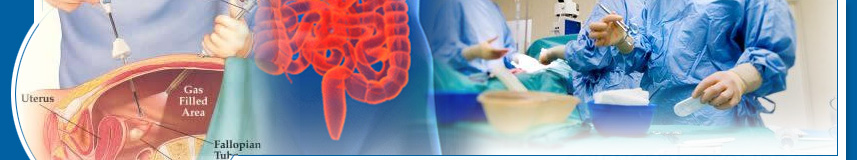
What is laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is one type of minimally invasive surgery. It is commonly referred to as:
- Keyhole surgery
- Band-aid Surgery
- Pinhole Surgery
- Endoscopy
Laparoscopy involves small incisions and is most commonly done under general anesthesia at a surgery center or hospital. Patients typically go home the same day or the following morning unless the procedure requires more involved or advanced laparoscopic surgery, possibly in colon surgery, for instance, and in some urogynecologic procedures
What are the advantages of laparoscopy and minimally invasive surgery?
- Reduced blood loss during and after surgery, therefore, reducing the chance of a blood transfusion
- Reduced adhesions or scar tissue postoperatively
- Smaller and fewer incisions
- Less pain postoperatively, therefore, less pain medication needed postop
- Reduced hospital stay
- Reduced exposure of internal organs (less exposure to more traumatic instrumentation during surgery and glove powder) and air that can create dryness and therefore possibly create adhesions
- Reduced risk of infection
What kinds of operations can be performed using laparoscopic surgery?
Most intestinal surgeries can be performed using the laparoscopic technique. These include surgery for ulcerative colitis, diverticulitis, cancer, rectal prolapsed and severe constipation.
In the past there had been concern raised about the safety of laparoscopic surgery for cancer operations. Recently several studies involving hundreds of patients have shown that laparoscopic surgery is safe for certain colorectal cancers.
How safe is laparoscopic surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery is as safe as traditional open surgery. At the beginning of a laparoscopic operation the laparoscope is inserted through a small incision near the belly button (umbilicus). The surgeon initially inspects the abdomen to determine whether laparoscopic surgery may be safely performed. If there is a large amount of inflammation or if the surgeon encounters other factors that prevent a clear view of the structures the surgeon may need to make a larger incision in order to complete the operation safely.
Any intestinal surgery is associated with certain risks such as complications related anesthesia and bleeding or infectious complications. The risk of any operation is determined in part by the nature of the specific operation. An individual’s general heath and other medical conditions are also factors that affect the risk of any operation. You should discuss with your surgeon your individual risk for any operation.
|