 The “diabetic foot” may be a perfect disease state for disease management. The “diabetic foot” may be a perfect disease state for disease management.
Diabetic foot disease management involves a combination of targeting the right population for prevention services and treating foot complications based on evidence-based treatment protocols.
Fifteen to 25% of diabetic patients develop a foot ulcer at some time during their life and 40–80% of these ulcers become infected.
The patho-physiological mechanisms of diabetic foot infections are still a subject of controversy.
The various hypotheses proposed include:
• A deficiency of cell-mediated immune mechanisms accentuated by hyperglycemia that can alter leukocyte functions,
• The harmful effects of neuropathy and excessive pressure on the wound,
• The chronic nature of the lesion,
• Hypoxia, due to a poor local perfusion and accentuated by the host’s hypermetabolic state and microbial cellular metabolism. Hypoxia promotes anaerobic subcutaneous infections and decreases the bactericidal activity of neutrophils,
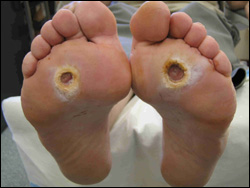 • Arterial disease decreasing the blood supply to the wound and consequently the influx of endogenous and exogenous factors (antibiotics) involved in the fight against infection, • Arterial disease decreasing the blood supply to the wound and consequently the influx of endogenous and exogenous factors (antibiotics) involved in the fight against infection,
• The particular anatomy of the foot, divided into several compartments, explaining the rapid spread of infection.
Risk Factor:
- Hallmarks: gross infection and late presentation
- Due to: bare foot gait, attempts at home Surgery, trust in faith healers and undetected diabetes.
- Other factors: ill fitting footwear – foot deformity, improper toe-nail cutting, use of chappal with single throng, etc.
|

