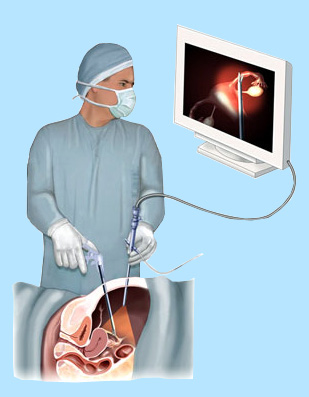
Laparoscopy is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis through small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. It can either be used to inspect and diagnose a condition or to perform surgery.
 Types: Types:
There are two types of laparoscope:
(1) a telescopic rod lens system, that is usually connected to a video camera (single chip or three chip), or
(2) a digital laparoscope where the charge-coupled device is placed at the end of the laparoscope, eliminating the rod lens system.
Surgery:
The laparoscope allows doctors to perform both minor and complex surgeries with a few small cuts in the abdomen.
There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an open procedure. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions and hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time
Gynecological diagnosis:
In gynecology, diagnostic laparoscopy may be used to inspect the outside of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes, for example in the diagnosis female infertility. Usually, there is one incision near the navel and a second near to the pubic hairline.
For gynecological diagnosis a special type of laparoscope can be used, called a fertiloscope. A fertiloscope is modified to make it suitable for trans-vaginal application.
A dye test may be performed to detect any blockage in the reproductive tract, wherein a dark blue dye is passed up through the cervix and is followed with the laparoscope through its passage out into the fallopian tubes to the ovaries.
Pediatric Laparoscopy:
Although laparoscopy in adult age group is widely accepted, its advantages in pediatric age group is questioned. Benefits of laparoscopy appears to recede with younger age. Efficacy of laparoscopy is inferior to open surgery in certain conditions such as pyloromyotomy for infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Although laparoscopic appendiectomy has lesser wound problems than open surgery, the former is associated with more intra-abdominal abscesses.Recently Raveenthiran raised concerns about the quick adoption and undue promotion of this technique in children. |
